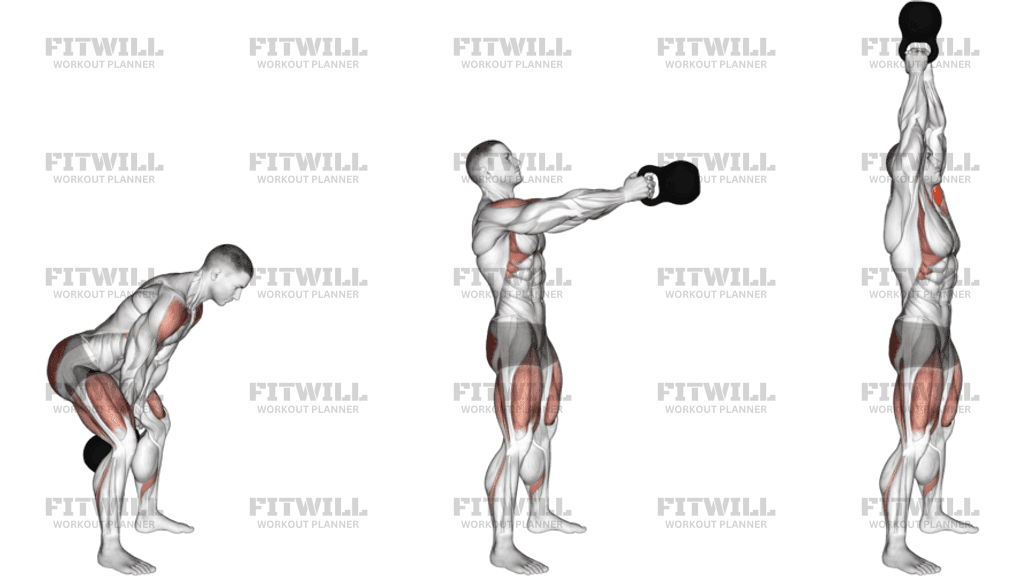
Ever wondered why kettlebell swings are all the rage in fitness circles? If you’re curious about what makes this dynamic movement so effective, you’re in the right place.
Kettlebell swings are not just about swinging a heavy weight back and forth; they’re a powerhouse of muscle engagement. But what muscles do kettlebell swings work, exactly? Imagine unlocking a workout that targets multiple muscle groups in one fluid motion.
Picture your core getting stronger, your glutes firing up, and your shoulders becoming more defined—all with a single piece of equipment. Sounds enticing, right? We’ll dive into the specific muscles that kettlebell swings activate. Understanding this can transform your workout routine, helping you achieve those fitness goals faster. Ready to discover the full potential of kettlebell swings? Keep reading, and let’s unravel the muscle magic together!
Primary Muscles Engaged
Kettlebell swings are a powerful exercise that targets several key muscles. They help build strength and endurance.
This move mainly works the muscles in your hips, legs, and core. These muscles work together to create the swinging motion.
Glutes Activation
The glutes are the largest muscles in your buttocks. They provide the main power for kettlebell swings.
When you swing the kettlebell, your glutes contract to push your hips forward. This action generates the force needed to lift the weight.
- Gluteus maximus is the primary muscle used
- Helps extend hips during the upward swing
- Supports posture and balance throughout the move
Hamstrings Role
The hamstrings are the muscles at the back of your thighs. They work with the glutes to control hip movement.
During kettlebell swings, the hamstrings help bend your knees and extend your hips. They also slow down the swing to keep it smooth.
- Includes biceps femoris, semitendinosus, and semimembranosus
- Controls hip hinge and knee flexion
- Helps prevent injury by stabilizing the legs
Core Stability
Your core muscles keep your body steady during kettlebell swings. They protect your spine and improve balance.
The core includes the abs, obliques, and lower back muscles. These muscles contract to stop your body from bending or twisting too much.
- Rectus abdominis helps with forward flexion
- Obliques control rotation and side bending
- Erector spinae supports the lower back
Secondary Muscles Involved
Kettlebell swings mainly work your hips and legs. They also activate several secondary muscles. These muscles help stabilize and support your body during the movement.
Understanding these secondary muscles can help improve your form. It also shows how kettlebell swings benefit your whole body.
Lower Back Support
Your lower back muscles help keep your spine stable during kettlebell swings. They prevent injury by supporting your torso as you move.
Strong lower back muscles make it easier to control the kettlebell. They also help maintain good posture throughout the exercise.
- Erector spinae muscles support the spine
- Help prevent rounding of the back
- Assist in transferring power from hips to upper body
Shoulder Engagement
Your shoulders work to guide and control the kettlebell swing. They help keep the kettlebell on the right path.
Muscles around the shoulder joint contract to stabilize your arms. This action helps avoid unnecessary swinging or jerking.
- Deltoids aid in lifting and controlling the kettlebell
- Rotator cuff muscles stabilize the shoulder joint
- Trapezius muscles help with upper back posture
Forearm And Grip Strength
Your forearm muscles work hard to hold the kettlebell handle firmly. Good grip strength prevents the kettlebell from slipping.
Strong forearms also reduce fatigue during multiple swings. They support better control and safety.
- Flexor muscles help close the hand around the handle
- Extensor muscles assist in wrist stability
- Improves overall hand and wrist endurance
Muscle Coordination And Movement
Kettlebell swings use many muscles working together. This exercise helps improve muscle coordination and body movement.
The swing is a full-body movement that trains muscles to work as a team. It builds strength and balance.
Hip Hinge Mechanics
The hip hinge is the main movement in kettlebell swings. It means bending at the hips, not the waist.
This motion activates the glutes, hamstrings, and lower back muscles. These muscles work together to move the hips powerfully.
- Glute muscles extend the hips
- Hamstrings help control the bend
- Lower back stabilizes the spine
Explosive Power Generation
Kettlebell swings build explosive power by training fast muscle contractions. The hips snap forward quickly.
This power comes from a strong push by the glutes and hips. It helps improve speed and strength in other exercises.
- Fast hip extension generates force
- Core muscles brace to transfer power
- Shoulders control the kettlebell path
Posture And Balance
Kettlebell swings improve posture by strengthening the back and core muscles. These muscles keep the body upright.
Balance improves as the body learns to control the kettlebell’s movement. This helps prevent injuries and builds stability.
- Core muscles keep the spine stable
- Back muscles support an upright posture
- Leg muscles adjust to maintain balance

Benefits For Full Body Strength
Kettlebell swings work many muscles in the body at once. They help build strength and power.
This exercise targets the legs, core, back, and shoulders. It is great for full body strength training.
Improved Athletic Performance
Kettlebell swings increase power and speed. They improve your ability to jump, run, and lift.
- Strengthens hips and glutes for explosive movements
- Builds core stability for better balance
- Enhances grip strength for sports
Enhanced Endurance
This exercise improves your heart and lung capacity. It helps you work longer without getting tired.
| Muscle Group | Role in Endurance |
| Hamstrings | Support continuous leg movement |
| Core | Maintain posture during long activity |
| Shoulders | Assist in repeated arm swings |
| Back | Stabilize spine under fatigue |
Injury Prevention
Kettlebell swings help protect joints and muscles from injury. They improve movement patterns.
- Strengthen lower back to reduce strain
- Improve hip mobility and flexibility
- Enhance muscle coordination and control
Common Mistakes Affecting Muscle Use
Kettlebell swings are a great exercise to work many muscles at once. But some mistakes can reduce their benefits. These errors change which muscles do the work.
Knowing these common mistakes helps you use the right muscles. This guide looks at three key errors and how they affect muscle use.
Overusing The Arms
Many beginners pull the kettlebell with their arms. This takes work away from the hips and legs. The arms should only guide the swing, not lift the weight.
- Using arms too much tires the shoulders and arms.
- It limits power from the hips and glutes.
- It can cause poor form and injury risk.
- Less core and lower body muscle activation occurs.
Rounding The Back
Keeping a straight back is important. Rounding the back puts strain on the spine and reduces muscle work in the hips and core. It also lowers exercise safety.
| Effect | Muscle Impact |
|---|---|
| Rounded Back | Less engagement of spinal erectors and core muscles |
| Neutral Spine | Better activation of core and back stabilizers |
Incorrect Hip Movement
Hips must drive the swing by snapping forward quickly. Wrong hip movement means less power and less muscle use. Some swing by squatting or lifting with the legs.
- Do not squat down; hinge at the hips.
- Snap hips forward to create momentum.
- Avoid lifting with the knees or quads only.
- Use glutes and hamstrings to power the swing.
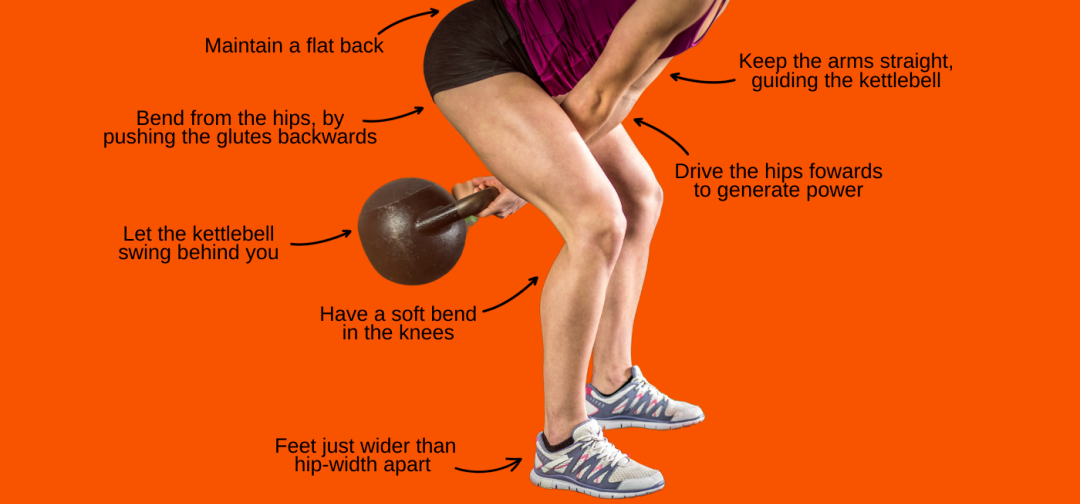
Tips To Maximize Muscle Engagement
Kettlebell swings work many muscles in your body. To get the best results, you need to use the right techniques. This helps you build strength and avoid injuries.
Focus on how you move, pick the right weight, and try different swings. These tips will help you engage your muscles better.
Proper Form Techniques
Keep your back straight and chest up during the swing. Bend your knees slightly and use your hips to drive the movement. Avoid using your arms to lift the kettlebell.
Engage your core muscles to protect your lower back. Breathe out as you swing up and breathe in as the kettlebell comes down.
- Stand with feet shoulder-width apart
- Push hips back, not down
- Use hip thrust to swing the kettlebell
- Keep arms relaxed and straight
- Engage your glutes and hamstrings
Choosing The Right Weight
Select a kettlebell weight that challenges you but lets you keep good form. Start with a lighter weight if you are new. Increase the weight slowly as you get stronger.
Using too heavy a kettlebell can cause poor form and risk injury. A weight that is too light will not fully engage your muscles.
- Beginners: 8-12 kg (18-26 lbs)
- Intermediate: 12-16 kg (26-35 lbs)
- Advanced: 16-24 kg (35-53 lbs)
Incorporating Variations
Try different kettlebell swing styles to work muscles in new ways. Variations can help prevent boredom and improve muscle strength.
Examples include single-arm swings, alternating swings, and double kettlebell swings. Each type targets muscles slightly differently.
- Single-arm swings improve balance and core stability
- Alternating swings increase coordination
- Double kettlebell swings build more power
- Russian swings focus on hip hinge and glutes
Frequently Asked Questions
What Primary Muscles Do Kettlebell Swings Target?
Kettlebell swings primarily target the glutes, hamstrings, and core. They also engage the lower back and hips, making it a full-body exercise that improves strength and power.
How Do Kettlebell Swings Benefit The Core Muscles?
Kettlebell swings engage the core to stabilize the spine during movement. This strengthens abdominal muscles and improves overall balance and posture, enhancing core endurance and functional fitness.
Are Kettlebell Swings Effective For Building Lower Body Strength?
Yes, kettlebell swings effectively build lower body strength. They focus on the glutes, hamstrings, and quads, improving muscle tone, power, and endurance in the hips and legs.
Do Kettlebell Swings Work The Upper Body Muscles Too?
Kettlebell swings engage the shoulders, traps, and forearms for control and stability. While the upper body is not the main focus, it still benefits from increased muscular endurance.
Conclusion
Kettlebell swings target many muscles at once. They work your hips, glutes, hamstrings, and core. Your back and shoulders also get stronger. This exercise helps improve power and endurance. It’s simple but very effective. Try adding kettlebell swings to your routine.
Feel your body grow stronger and more balanced. Keep your form steady and controlled. Small efforts bring big results over time. Stay consistent, and enjoy the benefits.